

can tell you about more advanced areas such as analytic geometry and topology. We will begin by studying each of three figures created in this manner. Geometry calculators for: plane and solid geometry, coordinate geometry. Refer to video for solution: John Galbraith (j5galbrauwaterloo. The equation of a circle with radius r and centre (0 0) has equation x2 + y2 r2. In this chapter, we will investigate the two-dimensional figures that are formed when a right circular cone is intersected by a plane. Proofs in Analytic Geometry (ii)Prove, using analytic geometry, that the angle inscribed in a semi-circle is 90. Intersection of median is called centroid of triangle and can be determined as 1 2 3 1 2 3, 3 3 x x x y y y+ + + + See proof at page 184 … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … ≥ Centre of In-Circle (In-Centre) Let ( )1 1,A x y, ( )2 2,B x y and ( )3 3,C x y are vertices of triangle. Of particular interest are the influences of Saturns moons and moonlets, and the ways they both disrupt and preserve the ring structure.

1 2: 1:1k k = then coordinate of C becomes 1 2 1 2, 2 2 x x y y+ + . Explanation: The general formula for a circle. The coordinates of the point C dividing the line segment AB in the ratio 1 2:k k are 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 2 ,k x k x k y k y k k k k + + + + If C be the midpoint of AB i.e. If this circle is moved to the left 2 spaces and down 3 spaces, where does the center of the new circle lie.
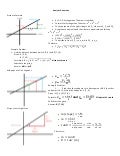
It is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way. Analytic Geometry is a branch of algebra that is used to model geometric objects - points, (straight) lines, and circles being the most basic of these.
#Analytic geometry formulas pdf#
Download Analytics Geometry Cheat Sheet and more Analytical Geometry Cheat Sheet in PDF only on Docsity!1 Introduction to Analytics Geometry Calculus and Analytic Geometry, MATHEMATICS 12 ≥ Distance Formula Let 1 1(, )A x y and 2 2(, )B x y be two points in a plane and d be a distance between A and B then 2 22 1 2 1( ) ( )d x x y y= − + − or 2 21 2 1 2( ) ( )d x x y y= − + − See proof on book at page181 … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … … ≥ Ratio Formula Let 1 1(, )A x y and 2 2(, )B x y be two points in a plane. Questions on the use of algebraic techniques for proving geometric facts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
